|
bitertanol
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: triazole
NOMENCLATURE
Common name bitertanol (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
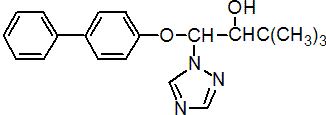
IUPAC name 1-(biphenyl-4-yloxy)-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol (20:80 ratio of (1RS,2RS) and (1RS,2SR) isomers)
Chemical Abstracts name b-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yloxy)-a-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
CAS RN [70585-36-3] diastereoisomer A; [70585-38-5] diastereoisomer B; [55179-31-2] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 259-513-5 Development codes KWG 0599 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Bitertanol is a mixture of 2 diastereoisomers. Enantiomer A: (1R,2S) + (1S,2R); enantiomer B: (1R,2R) + (1S,2S) in the ratio A:B 8:2. Mol. wt. 337.4 M.f. C20H23N3O2 Form White powder; (tech., white to tan crystals with a mild odour). M.p. 138.6 ºC (A), 147.1 ºC (B), 118 ºC (eutectic of A and B) V.p. 2.2 ´ 10-7 mPa (A); 2.5 ´ 10-6 mPa (B) (both 20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.1 (A), 4.15 (B) (both 20 ºC) Henry 2 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (A); 5 ´ 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (B) (both 20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.16 (20 °C) Solubility In water 2.7 (A), 1.1 (B), 3.8 (eutectic) (all in mg/l, 20 ºC, not affected by pH). In dichloromethane >250, isopropanol 67, xylene 18, n-octanol 53 (all for sum of A and B, in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in neutral, acidic, and alkaline media; DT50 at 25 ºC >1 y (pH 4, 7 and 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by W. Brandes et al. (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1979, 32, 1). Introduced by Bayer AG and first marketed in 1980. Patents DE 2324010 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Steroid demethylation inhibitor. Mode of action Foliar fungicide with protective and curative action. Inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis. Acts on spore germination, mycelium development, and sporulation. Uses Control of scab and Monilinia diseases on fruit (at 156-938 g/ha); rusts and powdery mildews on ornamentals (125-500 g/ha); black spot on roses (125-750 g/ha); Sigatoka on bananas (105-195 g/ha); and leaf spot and other diseases of vegetables, cucurbits, cereals, deciduous fruit, peanuts, soya beans, tea, etc. As a seed dressing, control of smuts and bunts of wheat (4-38 g/dt) and rye (19-84 g/dt); in combination with other fungicides, also against seed-borne snow mould. Phytotoxicity Fruit crops are more tolerant to the wettable powder formulation than the emulsifiable concentrate formulation. Formulation types AE; DC; DS; EC; FS; LS; PA; SC; WP; WS. Selected products: 'Baycor' (Bayer CropScience); 'Proclaim' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Gaucho Bl? (+ imidacloprid+ anthraquinone) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sibutol A' (+ anthraquinone) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Baycoral' (Bayer CropScience); 'Baymat' (Bayer CropScience); 'Blast' (Vapco); 'Zaron' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Bayflor Duo' (+ cyfluthrin) (Bayer CropScience, Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cereline Secur' (+ fuberidazole+ imidacloprid+ triadimenol) (UK) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sibutol Secur' (+ fuberidazole+ imidacloprid) (UK) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sibutol' (+ fuberidazole) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Bacseal' * (+ 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate) (pruning paint) (Bayer); 'Cereline' * (+ fuberidazole+ triadimenol) (Bayer); 'Domestin' * (+ fuberidazole+ triadimenol) (Bayer); 'Ferial Bl? * (+ imidacloprid+ anthraquinone) (Bayer); 'Sibutol MZA' * (+ mancozeb+ anthraquinone) (Bayer); 'Zaron Combi' * (+ mancozeb+ anthraquinone) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis details available from Bayer CropScience. Residue analysis by glc (R. Brennecke, Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. Bayer, 1985, 38, 33; W. Specht & M. Tillkes, ibid., 1980, 33, 61) or by hplc (R. Brennecke, ibid., 1988, 41, 113). Methods for the determination of residues are also available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000, mice c. 4300, dogs >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.55 mg/l air (aerosol), >1.2 mg/l air (dust). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 100 mg/kg diet. In 12/20 mo trials, NOEL for dogs 25 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 776, for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg b.w. LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks >5000, for bobwhite quail 808 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 2.14, for bluegill 3.54 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 1.8-7 mg/l. Algae ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 6.52 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral ) >104.4 mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The excretion of the parent compound and its biotransformation products is rapid, and occurs mainly via the faeces. Bitertanol exhibits no potential for accumulation.. Plants The concentration of bitertanol in plant tissues is negligible. The active ingredient could be determined on the surface of fruits and leaves of treated plants. Soil/Environment Direct photodegradation in water contributes to overall degradation of bitertanol to only a low extent. Environmental DT50 in water is 1 mo to 1 y. Degradation in soil is rapid; CO2 is the most important metabolite. Mobility in soil is low.
|