|
bifenthrin
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name bifenthrin (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO); bifenthrine ((f) draft F-ISO)
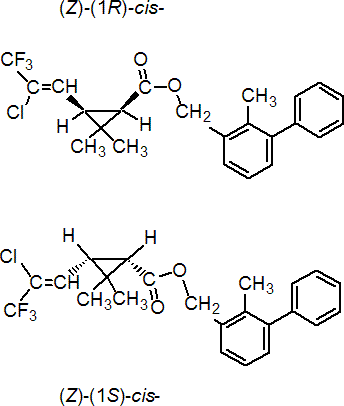
IUPAC name 2-methylbiphenyl-3-ylmethyl (Z)-(1RS,3RS)-3-(2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoroprop-1-enyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Roth: 2-methylbiphenyl-3-ylmethyl (Z)-(1RS)-cis-3-(2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoroprop-1-enyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name (2-methyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl)methyl 3-(2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoro-1-propenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [82657-04-3] Development codes FMC 54 800 Official codes OMS 3024
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Material contains ³97% cis- isomer, £3% trans- isomer. Mol. wt. 422.9 M.f. C23H22ClF3O2 Form Viscous liquid; crystalline or waxy solid. M.p. 68-70.6 °C V.p. 0.024 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP >6 Henry 1.02 ´ 102 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.210 (25 ºC) Solubility In water <1 mg/l. Soluble in acetone, chloroform, dichloromethane, diethyl ether, and toluene. Slightly soluble in heptane and methanol. Stability Stable for 2 y at 25 ºC and 50 ºC (tech.). In natural daylight, DT50 255 d; stable 21 d at pH 5-9 (21 ºC). F.p. 165 ºC (Tag open cup); 151 ºC (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide and acaricide reported by H. J. H. Doel et al. (Meded. Fac. Landbouwwet. Rijksuniv. Gent, 1984, 49, 929) and A. R. Crossman et al. (ibid., p. 939). Introduced by FMC Corp. Manufacturers FMC; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Contact and stomach action. Uses Effective against a broad range of foliar pests, including Coleoptera, Diptera, Heteroptera, Homoptera, Lepidoptera and Orthoptera; it also controls some species of Acarina. Crops include cereals, citrus, cotton, fruit, grapes, ornamentals and vegetables. Rates range from 5 g/ha against Aphididae in cereals to 45 g/ha against Aphididae and Lepidoptera in top fruit. Formulation types EC; GR; SC; UL; WP. Compatibility Not compatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Talstar' (FMC)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aripyreth' (termites) (FMC, Nihon Nohyaku); 'Biflex' (FMC); 'Brigade' (FMC); 'Capture' (FMC); 'Semafor' (FMC); 'Starion' (FMC)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc; hplc for analysis of isomer content. Residue analysis by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 998.01). Details available from FMC Agricultural Chemicals Group. Analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 54.5 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin; virtually non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). No skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). NOEL (1 y) for dogs 1.5 mg/kg daily. Non-teratogenic in rats (£2 mg/kg daily) and rabbits (8 mg/kg daily). ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg [1992]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1800, mallard ducks 2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 4450, mallard ducks 1280 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.00035, rainbow trout 0.00015 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.00016 mg/l. Low solubility in water and high affinity for soil contribute to produce little impact in aquatic systems under field conditions. Bees LD50 (oral) 0.1 mg/bee; (contact) 0.01462 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Soil DT50 65-125 d. Koc 1.31-3.02 ´ 105.
|