|
bensultap
Insecticide
IRAC 4C; 2-dimethylaminopropane-1,3-dithiol
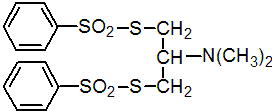
NOMENCLATURE
Common name bensultap (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name S,S'-2-dimethylaminotrimethylene di(benzenethiosulfonate)
Chemical Abstracts name S,S'-[2-(dimethylamino)-1,3-propanediyl] di(benzenesulfothioate)
CAS RN [17606-31-4] Development codes TI-78 (Takeda); TI-1671 (Takeda) Official codes OMS 3011
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 431.6 M.f. C17H21NO4S4 Form Pale yellow crystalline powder with slight characteristic odour. M.p. 81.5-82.9 °C V.p. <1 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 2.28 (25 °C) S.g./density 0.791 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.448 mg/l (20 °C). In hexane 0.319, toluene 83.3, dichloromethane >1000, methanol 10.48, ethyl acetate 149 (all g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable £150 ºC under dispersed light and at pH <5 (room temperature), but hydrolysed in neutral or alkaline solution (DT50 £15 min, pH 5-9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide developed by Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. (now Sumitomo Chemical Takeda Agro Company Ltd) and first marketed in 1983. Manufacturers Sumitomo Chemical Takeda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Analogue or propesticide of the natural toxin nereistoxin. Acts as a synaptic blocking agent for the insect central nervous system. Inhibits the action of synaptic transmitter (acetylcholine) by occupying the post-synaptic membrane where the acetylcholine receptor exists. Mode of action Insecticide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of major agricultural insect pests, particularly Coleoptera and Lepidoptera. In particular, control of Colorado beetles in potatoes and aubergines; tea leaf rollers and yellow tea thrips in tea; rice stem borers, rice leaf rollers, rice leaf miners and rice leaf beetles in rice; Oriental corn borers and Tanymecus spp. in maize; Tanymecus spp., root weevils, and tortoise beetles in beet; grape berry moths on vines; leaf beetles in cereals; boll weevils in cotton; codling moths, blister moths, and leaf miners in apples; small cabbage-white butterfly larvae, diamond-back moths, and blossom rape beetles on brassicas and oilseed rape; etc. Typical application rate is in the range 0.25-1.5 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity May be phytotoxic to certain varieties of apple, peach and citrus. Formulation types DP; GR; WP. Compatibility Not compatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Bancol' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Victenon' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Ruban' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'ZZ-Doricide' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 17). Residues determined by glc with FPD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1105, female rats 1120, male mice 516, female mice 484 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.47 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 250, male mice 40, female mice 300 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for rats 10, mice 3.4-3.6 mg/kg b.w. daily. Non-oncogenic, non-teratogenic, and non-mutagenic. Other Acute i.p. LD50 for male rats 503, female rats 438, male mice 442, female mice 343 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 311 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail 1784, mallard ducks 3112 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 15, guppy 17, goldfish 11, rainbow trout 0.76 mg/l. LC50 (72 h) for carp 8.2, guppy 16, goldfish 7.4, rainbow trout 0.76 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (6 h) 40 mg a.i. (as EC)/l. Bees Low toxicity to honeybees. LC50 (topical, 48 h) 25.9 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment DT50 in soil varies from 3-35 d, depending on soil type. Soil DT50 c. 7 d (upland conditions in laboratory).
|