|
benfluralin
Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; dinitroaniline
NOMENCLATURE
Common name benfluralin (BSI, E-ISO); benfluraline ((f) F-ISO); benefin (WSSA); bethrodine (JMAF)
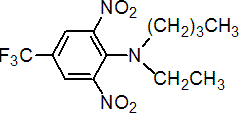
IUPAC name N-butyl-N-ethyl-a,a,a-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-p-toluidine
Chemical Abstracts name N-butyl-N-ethyl-2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzenamine
CAS RN [1861-40-1] EEC no. 217-465-2 Development codes EL-110 (Lilly)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 335.3 M.f. C13H16F3N3O4 Form Yellow-orange crystals. M.p. 65-66.5 ºC B.p. 121-122 ºC/0.5 mmHg; 148-149 ºC/7 mmHg V.p. 8.76 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.29 (20 ºC, pH 7) Henry 29.4 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.28 (20 ºC) (tech.) Solubility In water 0.1 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, chloroform >1000, toluene 330-500, acetonitrile 170-200, hexane 18-20, methanol 17-18 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Decomposed by u.v. light. Stable for up to 30 days at pH 5-9 (26 ºC). F.p. 151 °C (Setaflash closed cup; ASTM D-3278)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by J. F. Schwer (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1965). Introduced in USA (1963) by Eli Lilly & Co (agrochemical interests now Dow AgroSciences). Patents US 3257190 Manufacturers Budapest Chemical; Dintec; Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibition. Mode of action Selective soil herbicide, absorbed by the roots. Affects seed germination and prevents weed growth by inhibition of root and shoot development. Uses Control of annual grasses and some annual broad-leaved weeds in peanuts, lettuce, cucumbers, chicory, endive, field beans, french beans, lentils, alfalfa, clovers, trefoil, tobacco and established turf. Applied pre-emergence with soil incorporation, at 1.0-1.5 kg/ha. Formulation types EC; GR; WG. Selected products: 'Balan' (Dow AgroSciences, Platte); 'Benefex' (Makhteshim-Agan); mixtures: 'Team' (+ trifluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'XL-2G' (+ oryzalin) (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Balfin' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Banafin' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Banafine' (Dow AgroSciences, Bayer CropScience); 'Bonalan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Quilan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Saegreen' (Dow AgroSciences) mixtures: 'Banafine Pro' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Flural' * (Dow); 'Flubalex' * (Budapest Chemical)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by u.v. spectrometry (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1726; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 973.13) or by glc with FID (ibid., 973.14; CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1728). Residues by glc with ECD (W. S. Johnson & R. Frank, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 335). Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >10 000, mice >5000, dogs and rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Moderately irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) >2.16 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.5 mg/kg b.w. daily, for mice 6.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.005 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) II
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks, bobwhite quail, and chickens >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 for bluegill sunfish 0.065, rainbow trout 0.081, sheepshead minnow >1.1 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 2.18 mg/l. Algae For Selenastrum capricornutum (7 d), 3.86 mg/l reduced specific growth rate and terminal biomass by 16.6% and 34.3% respectively. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (shell deposition) for eastern oyster (Crassostrea variegatus) >1.1 mg/l; LC50 for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 0.043 mg/l. Bees Low toxicity; 33% formulation had no effect up to 100 ppm in 60% sucrose, but at 1000 ppm, mortality was increased.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Soil/Environment Soil DT50 (anaerobic) 15 d, (aerobic) 2.8 w to 1.7 mo; aquatic DT50 (anaerobic) 38.4 h; soil photolysis DT50 12.5 d. Duration of residual activity in soil is c. 4-8 mo. Likely to be relatively immobile in soil: Koc >5000; adsorption Freundlich K 27 in sandy soil (pH 7.7) to 117 in clay loam (pH 6.9).
|