|
benazolin
Herbicide
HRAC O WSSA 4; benzothiazolone
NOMENCLATURE
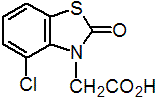
benazolin
Common name benazolin (BSI, E-ISO, WSSA, ANSI); bénazoline ((f) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 4-chloro-2-oxobenzothiazolin-3-ylacetic acid; 4-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxobenzothiazol-3-ylacetic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 4-chloro-2-oxo-3(2H)-benzothiazoleacetic acid
CAS RN [3813-05-6] EEC no. 223-297-0 Development codes RD 7693 (Boots)
benazolin-ethyl
Common name benazolin-ethyl
CAS RN [25059-80-7] EEC no. 246-591-0
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
benazolin
Composition Tech. grade is c. 90% pure. Mol. wt. 243.7 M.f. C9H6ClNO3S Form Colourless, odourless crystals. M.p. 193 ºC; (tech., 189 ºC) V.p. 1 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 1.34 (20 ºC) Henry 4.87 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 500 mg/l (pH 2.94, 20 ºC). In acetone 100-120, ethanol 30-38, ethyl acetate 21-25, isopropanol 25-30, dichloromethane 3.7, toluene 0.58, p-xylene 0.49, hexane <0.002 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in neutral, acidic, and weakly alkaline media. Decomposed by concentrated alkalis. pKa 3.04 (20 ºC)
benazolin-ethyl
Mol. wt. 271.7 M.f. C11H10ClNO3S Form White crystalline solid; (tech. is pale yellow crystalline powder with a characteristic odour). M.p. 79.2 ºC; (tech., 77.4 ºC) V.p. tech. 0.37 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 2.50 (20 ºC, in distilled water) S.g./density 1.45 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 47 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 229, dichloromethane 603, ethyl acetate 148, methanol 28.5, toluene 198 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to at least 300 ºC. Stable in acid and in neutral solution; at pH 9.18, DT50 7.6 d (25 ºC). No significant breakdown in water in natural sunlight.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by E. L. Leafe (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 7th, 1964, p. 32). Introduced by The Boots Co. Ltd (now Bayer CropScience). Patents GB 862226; GB 1243006 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid). Mode of action Selective, systemic, growth-regulator herbicide, absorbed principally by the leaves, and translocated readily throughout the plant in the phloem. Uses Post-emergence control of many annual broad-leaved weeds, particularly black bindweed (Bilderdykia convolvulus), common chickweed (Stellaria media), cleavers (Galium aparine), and charlock (Sinapis arvensis), in oilseed rape. In combination with other herbicides, used for control of a wider range of broad-leaved weeds in oilseed rape, cereals (non-undersown, and undersown with grass or clover), grassland, clover, alfalfa, and flax. With dicamba, benazolin exhibits a strong synergistic effect, giving improved control of a number of species, including mayweeds. Phytotoxicity Selective in cereals, oilseed rape, soya beans, maize, grassland. Formulation types EC; SC. Selected products: mixtures: 'Scorpion' (+ clopyralid+ dimefuron) (Bayer CropScience) Formulation types EC; SC.
OTHER PRODUCTS
benazolin
'Rescate' (CAS) mixtures: 'Asset' (+ bromoxynil+ ioxynil) (as salts) (Bayer CropScience); 'Setter' (+ MCPA+ 2,4-DB) (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Keropur' * (Aventis) mixtures: 'Scorpio' * (+ clopyralid+ dimefuron) (Bayer)
benazolin-ethyl
Mixtures: 'Benazalox' (+ clopyralid) (Bayer CropScience); 'Legumex Extra' (+ MCPA+ 2,4-DB) (salts) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Cresopur' * (AgrEvo); 'Galtak' * (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc or hplc. Residue analysis by glc. Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
benazolin
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000, mice >4000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Mild skin and eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 1.43 g/m3 air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 300-1000 mg/kg daily; for dogs c. 300 mg/kg daily. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xi; R36/38| R52, R53
benazolin-ethyl
Reviews Informationen zum Wirkstoff: Benazolin-ethyl, Industrieverband Agrar e.V., prepared by Schering AG (now Aventis). Public Access to Information on Pesticides, BAA Summary document: Benazolin-ethyl, prepared by Schering Agrochemicals (now Aventis). Oral Acute oral LD50 for mice >4000, rats >6000, dogs >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2100 mg/kg; not an irritant to skin and eyes of rabbits. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) >5.5 mg/l. Low acute toxicity by inhalation route. NOEL (2 y) for rats 12.5 mg/kg (0.61 mg/kg daily); (1 y) for dogs 500 mg/kg (18.6 mg/kg daily). ADI 0.006 mg/kg (dogs); 0.36 mg for a 60 kg human. EC classification N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
benazolin
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >10 200 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout 31.3, bluegill sunfish 27 mg/l. Daphnia Low toxicity; LC50 (48 h) 233.4 mg/l (measured); 353.6 mg/l (nominal). Bees Non-toxic. LD50 480 mg/bee.
benazolin-ethyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >6000, Japanese quail >9709, mallard ducks >3000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >20 000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 2.8, rainbow trout 5.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 6.2 mg/l. 21 d NOEC (immobilisation) 0.05 mg/l, (reproduction) 0.158 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 16.0 mg/l; NOEL 1.0 mg/l. Bees 10% EC formulation not harmful to bees. Worms Low toxicity to earthworms: >1000 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
benazolin
Animals In urine, major metabolites are N-[2-chloro-6-(methylsulfinyl)phenyl]glycine and N-[N-[2-chloro-6-(methylthio)phenyl]glycinyl]aniline. There are also small amounts of other acid-labile polar conjugates of benazolin acid, and N-[2-chloro-6-(methylthio)phenylglycine]. Faecal metabolites are similar to those in urine. Plants Benazolin acid is metabolised to form acid-labile conjugates. Minor pathways include hydroxylation of the aromatic ring of benazolin acid and loss of the acetic acid side-chain, followed by conjugation. Benazolin acid is translocated more rapidly and to a greater extent in sensitive species (e.g. mustard) than in resistant species (barley and rape). In barley, uptake and translocation are minimal and the majority of the applied material is recovered as parent compound at the site of application. Soil/Environment Degrades to principally 'bound residues'. DT50 c. 14-28 d. Kd 1.0 (sandy loam), 0.4 (loam).
benazolin-ethyl
Animals Metabolism is by de-esterification of benazolin-ethyl to benazolin with a minor pathway involving opening of the thiazoline ring. Plants The major metabolite is benazolin acid. Soil/Environment On soil surface exposed to light, DT50 3.5 d. In soil, DT50 1-2 d. Benazolin-ethyl is degraded in soil by hydrolysis of the ester followed by a loss of the acetic acid side-chain, then ring opening and sulfonation. The major degradates are benazolin acid and 4-chloro-2-oxobenzothiazolin. Kd 15 (sandy loam), 8 (loam).
|