|
azocyclotin
Acaricide
IRAC 12B; organotin acaricide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name azocyclotin (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ESA)
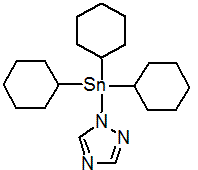
IUPAC name tri(cyclohexyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yltin; 1-tricyclohexylstannanyl-1H-[1,2,4]triazole
Chemical Abstracts name 1-(tricyclohexylstannyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole
CAS RN [41083-11-8] EEC no. 255-209-1 Development codes BAY BUE 1452 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 436.2 M.f. C20H35N3Sn Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 210 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 2 ´ 10-8 mPa (20 °C); 6.0 ´ 10-8 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.3 (20 °C) Henry 7 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C) (calc.) S.g./density 1.335 (21 °C) Solubility In water 0.12 mg/l (20 ºC). In dichloromethane 20-50, isopropanol 10-20, n-hexane 0.1-1, toluene 2-5 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability DT50 (22 ºC) 96 h (pH 4), 81 h (pH 7), 8 h (pH 9). pKa 5.36, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Acaricide reported by W. Kolbe (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1977, 30, 325). Introduced by Bayer AG in 1978. Patents DE 2143252 Manufacturers Cerexagri
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation; disruptor of ATP formation. Mode of action Long-acting acaricide with contact action. Uses Control of all motile stages of spider mites on fruit (including citrus), vines, hops, cotton, vegetables, and ornamentals. Formulation types SC; WP. Selected products: 'Peropal' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Clairmait' (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis details available from Bayer CropScience. Residue analysis by glc (E. Möllhoff, ibid., 1977, 30, 249).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 71 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 209, female rats 363, guinea pigs 261, mice 870-980 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg; strong dermal irritant; strong and corrosive eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 0.02 mg (as AE)/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 5, mice 15, dogs 10 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.007 mg/kg b.w. [1994] (with cyhexatin). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R26| T; R25| Xi; R37/38, R41| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male Japanese quail 144, female Japanese quail 195 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.004, golden orfe 0.0093 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.04 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus 0.16 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 >100 mg/bee (500 SC). Worms LC50 (28 h) 806 mg/kg (25 WP).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolised by hydrolysis, forming 1,2,4-triazole and tricyclohexyl tin hydroxide, which is further oxidised to form dicyclohexyl tin oxide. Plants Metabolites identified in plants include 1,2,4-triazole, tricyclohexyl tin hydroxide, and dicyclohexyl tin oxide. Soil/Environment Half-life in soil ranges from a few days to many weeks, depending on soil type.
|