|
azinphos-methyl
Insecticide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
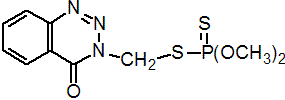
NOMENCLATURE
Common name azinphos-methyl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); azinphosmethyl (ESA); metiltriazotion * (former exception, USSR)
IUPAC name S-(3,4-dihydro-4-oxobenzo[d]-[1,2,3]-triazin-3-ylmethyl) O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-dimethyl S-[(4-oxo-1,2,3-benzotriazin-3(4H)-yl)methyl] phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [86-50-0] EEC no. 201-676-1 Development codes Bayer 17 147; R 1582; E1582 Official codes ENT 23 233; OMS 186
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 317.3 M.f. C10H12N3O3PS2 Form Yellowish crystals. M.p. 73 ºC V.p. 5 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 ºC); 1 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 2.96 Henry 5.7 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.518 (21 ºC) Solubility In water 28 mg/l (20 ºC). In dichloroethane, acetone, acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, dimethyl sulfoxide >250, n-heptane 1.2, xylene 170 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline and acidic media; DT50 (22 ºC) 87 d (pH 4), 50 d (pH 7), 4 d (pH 9). Photodegrades on soil surfaces and readily photodegrades in water. Decomposes above 200 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by E. E. Ivy et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1955, 48, 293). Developed by W. Lorenz and introduced by Bayer AG. European rights acquired by Makhteshim-Agan in 2002. Patents US 2758115; DE 927270 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; General Quimica; Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Non-systemic, with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of chewing and sucking insects of the orders Coleoptera, Diptera, Homoptera, Hemiptera, and Lepidoptera, on fruit trees (including citrus), vines, strawberries, nuts, vegetables, potatoes, cereals, maize, cotton, ornamentals, beet, soya beans, tobacco, rice, coffee, sugar cane, forestry, and other crops. Phytotoxicity Russetting is possible on some fruit varieties with the emulsifiable concentrate formulation. Formulation types DP; EC; SC; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Gusathion M' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Acifon' (General Quimica); 'Azín 200' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Azinugec' (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Cotnion-Methyl' (Makhteshim-Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Guthion' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Aziflo' (Chemia); 'Azin-PB' (Isagro); 'Crysthyon' (Crystal); 'Mezyl' (Papaeconomou); 'Sniper' (UAP); 'Supervelax' (IQV) Discontinued products: 'Valefos' * (Productos OSA)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by lc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 989.01, 7.7.02), by rplc (ibid., 989.01; CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 12) or by i.r. spectrophotometry (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 980.09; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 1970) or by colorimetric measurement of the phosphorodithioate moiety as a complex (ibid., 1970, 1, 25; FAO Specification CP/4). Residues determined by glc (Analyst (London), 1977, 102, 858; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733; D. H. MacDougall, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 397) or by spectrometry (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 961.12*, see 12th Ed., 29.102-29.107). Methods for the determination of residues are available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 62, 64 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 9, male guinea pigs 80, mice 11-20, dogs >10 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 150-200 mg/kg (24 h); not a skin irritant; mild eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.15 mg/l air (aerosol). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 5 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 5 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.005 mg/kg b.w. [1991]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R26/28| T; R24| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail c. 32 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for Japanese quail 935 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.02, golden orfe 0.12 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.0011 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus 7.15 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Worms LC50 (14 d) 59 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Azinphos-methyl is an effective insecticide, therefore an effect on some non-target arthropods cannot be excluded, in particular, where those organisms are directly exposed to the spray treatment.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In mammals, following oral administration, >95% is eliminated in the urine and faeces within 2 days. The major metabolites are the monodesmethyl compound and benzazimide. Plants In plants, major metabolites identified include azinphos-methyl oxon, benzazimide, mercaptomethyl benzazimide and cysteinmethyl benzazimide. Soil/Environment Degradation involves oxidation, demethylation, and hydrolysis. Based on the Koc values and leaching studies, azinphos-methyl can be classified as a compound with low mobility. The half-life in soil is several weeks.
|