|
azimsulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name azimsulfuron (BSI, pa E-ISO)
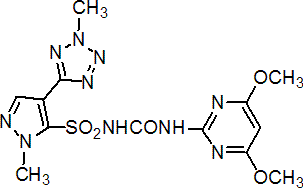
IUPAC name 1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-[1-methyl-4-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyrazol-5-ylsulfonyl]urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-1-methyl-4-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole-5-sulfonamide
CAS RN [120162-55-2] Development codes IN-A8947; DPX A8947 (DuPont); A8947; JS-458
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >98%. Mol. wt. 424.4 M.f. C13H16N10O5S Form White powdered solid, with a phenolic odour. M.p. 170 ºC V.p. 4.0 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 4.43 (pH 5), 0.043 (pH 7), 0.008 (pH 9) (all 25 °C) Henry 8 ´ 10-9 (pH 5); 5 ´ 10-10 (pH 7); 9 ´ 10-11 (pH 9) (all in Pa m3 mol-1, calc.) S.g./density 1.12 (25 °C) Solubility In water 72.3 (pH 5), 1050 (pH 7), 6536 (pH 9) (all in mg/l, 20 ºC). In acetone 26.4, acetonitrile 13.9, ethyl acetate 13.0, methanol 2.1, dichloromethane 65.9, toluene 1.8, hexane <0.2 (all in g/l, 25 °C). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 89 (pH 5), 124 (pH 7), 132 (pH 9) d (25 °C). Degradation was through cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge to give mainly the tetrazolylpyrazole sulfonamide and aminodimethoxypyrimidine. DT50 in irradiated aqueous solution, corrected for hydrolysis, was 103 (pH 5), 164 (pH 7), 225 (pH 9) d (25 °C). Indirect photodegradation has also been studied (A. C. Barefoot, Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds,1995, 2, 713). pKa 3.6
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by T. Marquez et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 1, 65). Patents US 4746353 Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Post-emergence herbicide with mainly foliar uptake; translocated in xylem and phloem. Initial symptoms are cessation of growth and chlorosis, followed by reddish colouration, then necrosis. Uses Post-emergence, selective control of Echinochloa spp. and other annual and perennial broad-leaved and sedge weeds in Southern European rice, at 20-25 g/ha. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Gulliver' (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Azin' (DuPont) mixtures: 'Bazooka 36' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cyhalofop-butyl+ thenylchlor) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Bazooka A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cyhalofop-butyl) (Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, Tokuyama, DuPont); 'Dancing A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ indanofan) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Dancing-Power A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ clomeprop+ indanofan) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Inebrite' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ fentrazamide) (Bayer CropScience); 'Kusastop A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ indanofan) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Masakari A Jumbo' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ clomeprop+ indanofan) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Papika A I Kilo' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cyhalofop-butyl+ thenylchlor) (Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, Tokuyama, Dow AgroSciences, DuPont); 'Papika A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cyhalofop-butyl+ thenylchlor) (Tokuyama, Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, DuPont, Dow AgroSciences); 'Weedless A36' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cafenstrole+ daimuron) (Sankyo Agro, DuPont, Eiko Kasei, SDS Biotech KK); 'Wydori A' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ dimethametryn+ pretilachlor) (Nihon Nohyaku) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Tabijin A' * (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cyhalofop-butyl+ pretilachlor+ pyriminobac-methyl) (Kumiai)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc/ms/ms (Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods, pp 400-410).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Not irritating to eyes or skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.84 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 34.3 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for male dogs 17.9 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.10 mg/kg b.w. Other Not mutagenic (Ames), not genotoxic, not carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U EC classification N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5260 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp >300, bluegill sunfish >1000, rainbow trout 154 ppm. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >1000 ppm; NOEC (21 d) >5.4 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 12 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for Lemna Gibba 0.8 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral) >25 mg/bee; (contact) >1000 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Following oral administration to rats, >95% azimsulfuron was excreted within 2 d, 60-73% in unmetabolised form. The major metabolic pathway was O-demethylation followed by pyrimidine ring hydroxylation and subsequent O-conjugation; a pyrimidine ring-cleaved guanidine was also identified; N-demethylation of pyrazole and tetrazole rings and cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge were also observed as minor routes. Plants Metabolism was rapid; little parent compound was found in any plant tissue at maturity. Soil/Environment Soil degradation in both flooded soils and under aerobic conditions has been studied. The most significant mechanisms are indirect photolysis and soil metabolism, together with chemical hydrolysis. Degradation products have been identified. No detectable residues in the field at harvest at depths of 0 to 50 cm. See A. C. Barefoot (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds,1995, 2, 713).
|