|
asulam
Herbicide
HRAC I WSSA 18; carbamate (DHP)
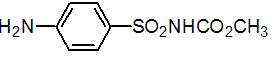
NOMENCLATURE
asulam
Common name asulam (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF); asulame ((m) F-ISO); no name (Germany)
IUPAC name methyl sulfanilylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl [(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]carbamate
CAS RN [3337-71-1] Development codes M&B 9057 (May & Baker)
asulam-sodium
Common name asulam-sodium
CAS RN [2302-17-2]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
asulam
Mol. wt. 230.2 M.f. C8H10N2O4S Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 142-144 ºC (decomp.) V.p. <1 mPa (20 ºC) Solubility In water 5 g/l (20-25 ºC). In dimethylformamide >800, acetone 340, methanol 280, methyl ethyl ketone 280, ethanol 120, hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons <20 (all in g/l, 20-25 ºC). Other salts: in water, potassium >400, ammonium >400, calcium >200, magnesium >400 (all in g/l, 20-25 ºC). Stability Stable in boiling water ³6 h. Stable >4 y (pH 8.5, room temperature). pKa 4.82, forming water-soluble salts
asulam-sodium
Mol. wt. 252.2 M.f. C8H9N2NaO4S Solubility In water >600 g/l (20-25 ºC)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. J. Cottrell & B. J. Heywood (Nature (London), 1965, 207, 655). Introduced by May & Baker Ltd (now Bayer CropScience). Patents GB 1040541 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Dow AgroSciences; High Kite; Synthesia
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibition of dihydropteroate synthase. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the leaves, shoots, and roots, with translocation in both the symplastic and apoplastic systems to other parts of the plant. Causes a slow chlorosis in susceptible plants. Uses Control of annual and perennial grasses and broad-leaved weeds in spinach, oilseed poppies, alfalfa, some ornamentals, sugar cane, bananas, coffee, tea, cocoa, coconuts, rubber, etc.; wild oats in flax; docks (Rumex spp.) in grassland, fruit trees and bushes, and on non-crop land; and bracken (Pteridium aquilinum) in grassland, non-crop land, and forestry. Application rates from 1-10 kg/ha, depending on crop. Formulation types SL.
asulam
Selected products: 'Sanulam' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
asulam
'Asilan' (Shionogi, Bayer CropScience); 'Fougerox' (Bayer CropScience)
asulam-sodium
'Asulox' (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 26; A. Guardigli et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 197) or by hydrolysis with colorimetry of a derivative (C. H. Brockelsby & D. F. Muggleton, ibid., 1973, 7, 497). Residues determined by the latter method (idem, ibid.) or by hplc of a derivative (A. Guardigli et al., loc. cit.).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews M. A. Gallo et al., Effect of asulam in wildlife species, residues and toxicity in bobwhite quail after prolonged exposure, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1975, 13(2), 200-205. B. Ingham & M. A. Gallo, Effect of asulam in wildlife species - acute toxicity to birds and fish, Proc. Northeast Weed Control Conf., 1975, (1), 194-199. Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats, mice, rabbits, and dogs >4000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >1200 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (6 h) for rats >1.8 mg/l air. NOEL In 90 d feeding trials, rats receiving 400 mg/kg diet showed no significant ill-effects. No effect observed when fed to cows at 800 ppm over 8 w, or to sheep at 50 mg/kg over 10 d. Non-teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
asulam
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks, pheasants, and pigeons >4000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout, channel catfish, and goldfish >5000, bluegill sunfish >3000, harlequin fish >1700 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees at <2% w/v by direct contact or ingestion.
asulam-sodium
Birds Acute oral LD50 for chickens, pigeons, quail >2000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 85-96% of the dose is eliminated, predominantly in the urine, within 3 days. Soil/Environment Has a short persistence in soil, DT50 c. 6-14 d. Soil metabolism is by loss of amino group, cleavage of carbamate group, or acetylation of amino group.
|