|
amitraz
Acaricide, insecticide
IRAC 19; amidine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name amitraz (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, ESA, BAN, JMAF); amitraze ((m) F-ISO)
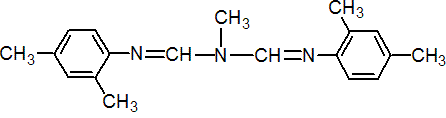
IUPAC name N-methylbis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)amine
Chemical Abstracts name N'-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N-[[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl]-N-methylmethanimidamide
Other names N,N-bis(2,4-xylyliminomethyl)methylamine; N-methyl-N'-2,4-xylyl-N-(N-2,4-xylylformimidoyl)formamidine; 1,5-di-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene CAS RN [33089-61-1] EEC no. 251-375-4 Development codes BTS 27 419 (Boots) Official codes OMS 1820; ENT 27 967
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 293.4 M.f. C19H23N3 Form White/pale yellow crystalline solid. M.p. 86-88 ºC V.p. 0.34 mPa (25 ºC) using clapeyron-clausius analysis KOW logP = 5.5 (25 ºC, pH 5.8) Henry 1.0 Pa m3 mol-1 (measured) S.g./density 1.128 (20 ºC) Solubility In water <0 .1 mg/l (20 ºC). Soluble in most organic solvents; in acetone, toluene, xylene >300 g/l. Stability Hydrolysis DT50 (25 ºC) 2.1 h (pH 5), 22.1 h (pH 7), 25.5 h (pH 9). U.V. light appears to have little effect on stability. pKa 4.2, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Acaricide reported by B. H. Palmer et al. (Proc. Int. Congr. Acarol. 3rd, 1971, p. 687) for veterinary use and by D. M. Weighton et al. (Meded. Fac. Landbouwwet. Rijksuniv. Gent, 1972, 37, 765) for crop use. Introduced by The Boots Co. Ltd.; (now marketed by Bayer CropScience for crop protection and by Hoechst AG for veterinary use). Patents GB 1327935 (Boots) Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Milenia; Rotam; Sharda; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Mode of action probably involves an interaction with octopamine receptors in the tick nervous system, causing an increase in nervous activity. Mode of action Non-systemic, with contact and respiratory action. Expellent action causes ticks to withdraw mouthparts rapidly and fall off the host animal. Uses Control of all stages of tetranychid and eriophyid mites, pear suckers, scale insects, mealybugs, whitefly, aphids, and eggs and first instar larvae of Lepidoptera on pome fruit, citrus fruit, cotton, stone fruit, bush fruit, strawberries, hops, cucurbits, aubergines, capsicums, tomatoes, ornamentals, and some other crops. Also used as an animal ectoparasiticide to control ticks, mites and lice on cattle, dogs, goats, pigs and sheep. Phytotoxicity At high temperatures, young capsicums and pears may be injured. Formulation types EC; PO; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials, parathion, and others. Selected products: 'Akaroff' (Ingeniería Industrial); 'Byebye' (Agriphar); 'Cekutraz' (Cequisa); 'Edrizar' (Siapa); 'Ovasyn' (Bayer CropScience); 'Parsec' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Rotraz' (Rotam); 'Sender' (Sanonda); 'Taktic' (veterinary use) (Intervet); 'Vapcozin' (Vapco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bemisit' (AgroSan); 'Dani-cut' (Nissan); 'Mitac' (crop protection) (Gowan); 'Mitisan' (Aragro); 'Tudy' (BASF) Discontinued products: 'Azadieno' * (Q.E.A.C.A.); 'Baam' * (Upjohn) mixtures: 'Synergin 1+2' * (+ tralomethrin) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1995, G, 5-10). Residue analysis also by glc. Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 650, mice >1600 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >200, rats >1600 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (6 h) for rats 65 mg/l air. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, no adverse effect observed in rats receiving 50-200 ppm diet, or in dogs dosed 0.25 mg/kg daily. Human NOEL >0.125 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail 788 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 7000, Japanese quail 1800 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.74, bluegill sunfish 0.45 mg/l. Due to rapid hydrolysis, it is unlikely that this toxicity will be expressed in natural aquatic systems. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.035 mg/l. Due to rapid hydrolysis, it is unlikely that this toxicity will be expressed in natural aquatic systems. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum >12 mg/l. Bees Low toxicity to bees and predatory insects. LD50 (contact) 50 mg/bee (formulation). Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg tech./kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapid breakdown leading to excretion as a conjugate of 4-amino-3-methylbenzoic acid and, to a lesser extent, to N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N'-methylformamidine. Plants Rapidly degraded, mainly to N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N'-methylformamidine and, to a smaller extent, to 2,4-dimethylformanilide. Soil/Environment Rapidly broken down in soil under aerobic conditions (J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1977, 42, 187; ibid. 1978, 44, 383); DT50 in soil <1 d. Degradation occurs more rapidly in acid than in neutral or alkaline soils. Very strongly adsorbed to soil; Koc c. 1000-2000.
|