|
allethrin [(1R)- isomers]
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name allethrin (BSI, E-ISO, ESA, JMAF); alléthrine ((f) F-ISO); palléthrine ((f) France); no name (Germany)
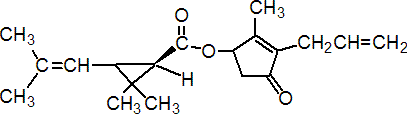
IUPAC name (RS)-3-allyl-2-methyl-4-oxocyclopent-2-enyl (1R,3R;1R,3S)-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
Alt: (RS)-3-allyl-2-methyl-4-oxocyclopent-2-enyl (+)-cis-trans-chrysanthemate
Roth: (RS)-3-allyl-2-methyl-4-oxocyclopent-2-enyl (1R)-cis-trans-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name 2-methyl-4-oxo-3-(2-propenyl)-2-cyclopenten-1-yl 2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methyl-1-propenyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [584-79-2] (unstated stereochemistry and also used for bioallethrin), formerly [137-98-4] EEC no. 209-542-4 [for (1RS)- isomers] Official codes OMS 468; ENT 17 510 [for (1RS)- isomers]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition d-Allethrin is ³95% (1R)- isomers and ³75% trans isomers; see also bioallethrin. Mol. wt. 302.4 M.f. C19H26O3 Form Tech. is a pale yellow liquid. B.p. 281.5 °C/760 mmHg V.p. 0.16 mPa (21 °C) KOW logP = 4.96 (room temperature) S.g./density 1.01 (20 °C) Solubility Practically insoluble in water. In hexane 0.655 g/ml, methanol 72.0 ml/ml (both 20 °C). Stability Decomposed by u.v. light. Hydrolysed in alkaline media. F.p. 87 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. S. Schechter et al. (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1949, 71, 3165). Development and properties reviewed by W. Barthel (Wld. Rev. Pest Control, 1967, 6, 59). Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. First registered in Japan in 1954. Manufacturers Jiangsu Yangnong; Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Gives rapid knockdown. Paralyses insects before killing them. Uses Control of flies, mosquitoes, ants, and other household and public health insect pests. Often used in combination with piperonyl butoxide or other synergists, for control of chewing and sucking insects on ornamentals, vegetables, and other crops; for household and public health insect control; for insect control in animal houses; and as an animal ectoparasiticide. Formulation types AE; EC; DP; MC; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Pynamin Forte' (Sumitomo)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Pynamin' (Sumitomo) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Pyrotex' * (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Protex SA)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 52) or by titration of a derivative (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 953.05*). The proportions of stereoisomers determined by glc of suitable derivatives (A. Murano, Agric. Biol. Chem., 1972, 36, 2203; F. E. Rickett, Analyst (London), 1973, 98, 687; A. Horiba et al., Agric. Biol. Chem., 1977, 41, 2003; 1978, 42, 671) or by nmr (F. E. Rickett & P. B. Henry, Analyst (London), 1974, 99, 330). Residues determined by glc (Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 283; J. Sherma, ibid., 1976, 8, 117). Details from McLaughlin Gormley King Co.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews See A. J. Gray & D. M. Soderlund, Chapt. 5 in "Insecticides". See also FAO/WHO 3, 4 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 2150, female rats 900 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rabbits 2660, female rabbits 4390 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 for rats >3875 mg/m3 air. ADI (JMPR) No ADI [1965]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail 5620 mg 'Pynamin Forte' /kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 0.134 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 87 (WHO, 1989). Animals In mammals, following oral administration, one of the two terminal methyl groups of the chrysanthemic acid moiety is oxidised in the liver to an alcohol group, and further to a carboxyl group.
|