|
aldicarb
Insecticide, acaricide, nematicide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
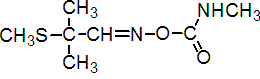
NOMENCLATURE
Common name aldicarb (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, ESA); aldicarbe ((m) F-ISO); no name (Germany)
IUPAC name 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyde O-methylcarbamoyloxime
Chemical Abstracts name 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propanal O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime
CAS RN [116-06-3] EEC no. 204-123-2 Development codes UC 21 149 (Union Carbide) Official codes OMS 771; ENT 27 093; AI3-27 093
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 190.3 M.f. C7H14N2O2S Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 98-100 ºC (tech.) V.p. 13 mPa (20 ºC) S.g./density 1.195 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 4.93 g/l (pH 7, 20 ºC). Soluble in most organic solvents, e.g. in acetone 350, dichloromethane 300, benzene 150, xylene 50 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Practically insoluble in heptane and in mineral oils. The sulfoxide has solubility >330 g/l in water. Stability Stable in neutral, acidic, and weakly alkaline media. Hydrolysed by concentrated alkalis. Decomposes above 100 ºC. Rapidly converted by oxidising agents to the sulfoxide, which is more slowly oxidised to the sulfone (aldoxycarb q.v.). F.p. Non-flammable
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. H. J. Weiden et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1965, 58, 154). Introduced by the Union Carbide Corp. (now Bayer CropScience). Patents US 3217037 Manufacturers Agrochem; Bayer CropScience; Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor; specifically designed to resemble O-acetylcholine structurally (L. K. Payne & M. H. J. Weiden, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1966, 14, 356). Metabolically activated to aldicarb sulfoxide. Mode of action Systemic, with contact and stomach action. Absorbed rapidly through the roots, with translocation acropetally. Uses Soil application for control of chewing and sucking insects (especially aphids, whitefly, leaf miners, and soil-dwelling insects), spider mites, and nematodes in glasshouse and outdoor ornamentals, sugar beet, fodder beet, strawberries, potatoes, onions, hops, vine nurseries, tree nurseries, peanuts, soya beans, citrus fruit, bananas, coffee, sorghum, pecans, cotton, sweet potatoes, sugar cane, and other crops. Formulation types GR. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Sanacarb' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Temik' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aldee' (Me2); 'Miret' (Agrochem); 'Sentry' (Bayer CropScience); 'Tranid' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Cardinal' (+ fipronil) (BASF); 'Regent Plus' (+ fipronil) (BASF); 'Trident' (+ fipronil) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectrophotometry (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 10; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 974.04). Residues determined by rplc (ibid., 985.23), by glc with FPD after oxidation to aldoxycarb (R. T. Krause, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1980, 63, 1114; R. R. Romine, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 147; J. H. Smelt et al., loc. cit., pp. 279, 293). Methods based on colorimetry of a derivative were also used (D. P. Johnson et al., J. Assoc. Off Anal Chem., 1966, 49, 399; D. F. Lee & J. A. Rougham, Analyst (London), 1971, 96, 798). In drinking water, by rplc and fluorimetry of liberated methylamine (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.06).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 53 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 0.93 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rabbits 20 mg/kg. Inhalation Rats were killed within 5 minutes by a dust concentration of 0.2 mg/l air. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 0.3 mg/kg daily were unaffected. ADI (JMPR) 0.003 mg/kg b.w. [1995]. Water GV 10 mg/l (TDI 4 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ia; EPA (formulation) I EC classification T+; R26/28| T; R24| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 71 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.88, bluegill sunfish 1.5 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 121 (WHO 1991), 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In rats, dogs and cows, absorbed rapidly and completely; >80% is excreted in the urine within 24 h, >96% within 3-4 d. Aldicarb is oxidised to the sulfoxide and sulfone, which undergo further metabolism. Metabolism of carbamate insecticides is reviewed (M. Cool & C. K. Jankowski in "Insecticides"). Plants In plants, the sulfur atom is oxidised to sulfoxide and sulfone groups. The highly soluble sulfoxide acts systemically on the plant, and is 10-20 times more active as a cholinesterase inhibitor than aldicarb itself. Further degradation leads to the formation of oximes, nitriles, amides, acids and alcohols which are present in the plant only in conjugated form. Soil/Environment In soil, the sulfur atom is oxidised to sulfoxide and sulfone groups. Further degradation leads to the formation of oximes, nitriles, amides, acids and alcohols. Rapidly degraded in acid soils (pH >7.0), less so at pH £5.5. For degradation in soil and water, see J. H. Smelt et al., Pestic. Sci., 1995, 44, 323, and refs. therein.
|