|
alachlor
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15; chloroacetamide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name alachlor (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF); alachlore ((m) F-ISO)
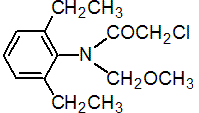
IUPAC name 2-chloro-2',6'-diethyl-N-methoxymethylacetanilide
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-N-(methoxymethyl)acetamide
CAS RN [15972-60-8] EEC no. 240-110-8 Development codes CP 50144 (Monsanto); MON 0144 (tech.) (Monsanto)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition ³93% pure. Mol. wt. 269.8 M.f. C14H20ClNO2 Form Yellow white to wine red, odourless solid (room temperature); yellow to red liquid (>40 °C). M.p. 40.5-41.5 ºC B.p. 100 °C/0.0026 kPa V.p. 2.0 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.09 Henry 3.2 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.1330 (25 °C) Solubility In water 170.31 mg/l (pH 7, 20 ºC). Soluble in diethyl ether, acetone, benzene, chloroform, ethanol, and ethyl acetate. Slightly soluble in heptane. Stability Hydrolysed by strong acids and alkalis. Stable to u.v. light. Decomposes at 105 ºC. F.p. 137 °C (closed cup); 160 °C (open cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by R. F. Husted et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1966, 21, 44). Introduced by Monsanto Co. Patents US 3442945; US 3547620 Manufacturers Comlets; Crystal; ÉMV; Krishi Rasayan; Makhteshim-Agan; Monsanto; Pilarquim; RPG; Sinon
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts by inhibition of protein synthesis and root elongation; more recent research suggests chloroacetamides may inhibit synthesis of very long chain fatty acids (J. Schmalfuss et al., Abstr. Meeting WSSA, Toronto, 40, 117-118, 2000; P. Böger, Abstr. III Int. Weed Control Congr., Brazil 2000). Maize tolerance is attributed to rapid detoxification by glutathione transferases. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed principally by germinating shoots, but also by the roots, with translocation throughout the plant, and accumulation mainly in vegetative parts rather than in reproductive parts. Uses Used pre-emergence at 1.68-4.48 kg/ha to control annual grasses and many broad-leaved weeds in cotton, brassicas, maize, oilseed rape, peanuts, radish, soya beans and sugar cane. Formulation types EC; GR; ME; WG. Selected products: 'Lasso' (Monsanto); 'Alanex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cattch' (RPG); 'Lacorn' (Efthymiadis); 'Satochlor' (ÉMV); 'Sholay' (Rallis); mixtures: 'Cotralin' (+ prometryn) (Efthymiadis)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Cropstar II' (Monsanto); 'Micro-Tech' (Monsanto); 'Partner' (Monsanto); 'Alac' (Chemia); 'Alagan' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Alanox' (Crystal); 'Chemiclor' (Chemiplant); 'Dipachlor' (Papaeconomou); 'Pilarzo' (Pilarquim); 'Shroud' (Cedar); 'Top 48' (Cequisa) mixtures: 'Bronco' (+ glyphosate-isopropylammonium) (Monsanto); 'Bullet' (+ atrazine) (Monsanto); 'Freedom' (+ trifluralin) (Monsanto); 'Lariat' (+ atrazine) (Monsanto); 'Alanex Pro' (+ prometryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Alanex TBA' (+ terbuthylazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Alazine' (+ atrazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Aracloro Super' (+ atrazine) (Aragro); 'Galirom' (+ oxyfluorfen) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Manager' (+ aclonifen) (Bayer CropScience); 'Propachlor Doble' (+ atrazine) (Probelte)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (J. M. Warner & D. D. Arras in Comp. Anal. Profiles, Chapt. 5; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 985.04, 988.03; CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D,4; ibid., 1992, E, 4). Residues in water and in soil determined by glc with ECD or FID; details, and other methods reviewed by J. M. Warner & D. D. Arras, loc. cit. In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 930-1350 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 13 300 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin or eyes (rabbits). Contact sensitisation reactions observed in guinea pigs. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.04 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs £1 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.01 mg/kg b.w. Water GV 20 mg/l (based on incidence of cancer in animals). Other Oncogenic in rats but not in mice; the mechanism of induction has been shown to be not relevant at anticipated exposure levels in humans. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R40| Xn; R22| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1536 mg/kg. LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.8, bluegill sunfish 2.8, fathead minnow 5.0, channel catfish 2.1 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 10 mg/l. Algae TL50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 12 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (48 h) for crayfish >320 mg/l. Bees Not hazardous to bees when used as directed; LD50 32 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 387 mg/kg dry soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly oxidised by rat liver microsomal oxygenases to 2,6-diethylaniline (Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 1989, 33, 16; J. Agric. Food Chem., 1989, 37, 1088; P. C. C. Feng et al., Drug Metab. Dispos., 1990, 18, 373). Plants Rapidly metabolised in plants to 2-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide, with further degradation to the aniline derivative. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil by microbial action to 2-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide, with further degradation to the aniline derivative; DT50 1-30 d. Persists in soil for c. 6-10 w (J. Tiedie et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1975, 23, 77; J. K. Lee, Hanguk Nanghwa Hakhoechi, 1986, 29, 182; Rev. Environm. Contam. Toxicol., 1989, 110, 110-114). In surface water, 55% degraded in 28 d.
|