|
acifluorfen-sodium
Herbicide
HRAC E WSSA 14; diphenyl ether
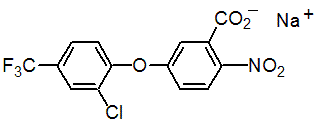
NOMENCLATURE
acifluorfen-sodium
Common name acifluorfen-sodium
IUPAC name sodium 5-(2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-nitrobenzoate
Chemical Abstracts name sodium 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoate
CAS RN [62476-59-9] EEC no. 263-560-7 Development codes RH-6201 (Rohm & Haas); MC 10978 (Mobil); BAS 9048.H (BASF)
acifluorfen
Common name acifluorfen (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); acifluorfène ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 5-(2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyloxy)-2-nitrobenzoic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 5-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoic acid
CAS RN [50594-66-6] EEC no. 256-634-5
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
acifluorfen-sodium
Composition Tech. salt is not generally isolated in solid form, but usually occurs as aqueous solution with 44% w/w a.i. Mol. wt. 383.6 M.f. C14H6ClF3NNaO5 Form Dry form is light yellow with a mildly antiseptic odour. M.p. (dry) 274-278 °C (decomp.) V.p. <0.01 mPa (25 °C) (evaporation rate method, CF/P006) KOW logP = 1.19 (pH 5, 25 °C) Henry <6.179 ´ 10-9 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density Bulk density 0.4-0.5 Solubility In water (unbuffered) 62.07, (pH 7) 60.81, (pH 9) 60.71 (all in g/100 g, 25 °C). In octanol 5.37, methanol 64.15, hexane <5 ´ 10-5 (all in g/100 ml, 25 °C). Stability Stable >2 y at 20-25 °C in aqueous solution. pKa 3.86?.12
acifluorfen
Mol. wt. 361.7 M.f. C14H7ClF3NO5 Form Light brown solid. M.p. 142-160 °C V.p. <0.01 mPa (20 ºC) (evaporation rate method, CF/P006) S.g./density 1.546 Solubility In water 120 mg/l (23-25 ºC) (tech.). In acetone 600, ethanol 500, dichloromethane 50, xylene, kerosene <10 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Decomposes at 235 ºC. Stable in acid and alkaline media, pH 3-9 (40 ºC). Decomposed by u.v. light, DT50 c. 110 h.
COMMERCIALISATION
History First registered in US in 1980. Introduced as a herbicide independently by Mobil Chemical Co. (now Bayer CropScience, who no longer market it) and by Rohm & Haas Co. (who transferred rights to BASF AG in 1987). Patents DE 2311638 Manufacturers Toll manufactured for BASF by Rohm & Haas Inc.
APPLICATIONS
acifluorfen-sodium
Biochemistry Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective contact herbicide, absorbed by the foliage and roots, with negligible translocation. Activity is enhanced by sunlight. Uses Used post-emergence for the control of annual broad-leaved weeds (Abutilon, Amaranthus, Datura, Euphorbia, Polygonum, Ipomoea, Xanthium spp.), with some effects on grasses in soya beans, peanuts and rice. Applied at 0.2 to 0.6 kg/ha, depending on crop. Phytotoxicity Soya beans show good tolerance, although some burning may be seen on new leaf growth, which is readily outgrown. Phytotoxicity increased if mixed with fertilisers. Formulation types SL. Compatibility Compatible with most other pesticides, but phytotoxicity to the crop may be increased with the addition of certain additives. Selected products: 'Blazer' (BASF); mixtures: 'Doble' (+ bentazone-sodium) (Latin America) (BASF); 'Galaxy' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF); 'Storm' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
acifluorfen-sodium
'Asif' (Sanonda) mixtures: 'Conclude B' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF); 'Conclude Ultra' (+ bentazone-sodium+ sethoxydim) (BASF); 'Conclude Xtra' (+ bentazone-sodium+ clethodim) (BASF) Discontinued products: 'Status' * (BASF); 'Tackle' * (Aventis) mixtures: 'Manifest B' * (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF); 'Scepter OT' * (+ imazaquin-ammonium) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residue analysis by glc or hplc (T. A. Ray et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1983,66, 1319).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
acifluorfen-sodium
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1540, female mice 1370, rabbits 1590 mg/kg b.w. (aqueous tech.). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Severe eye irritant; moderate skin irritant (rabbits) (aqueous tech.). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.91 mg/l air (aqueous formulation). NOEL for mice 7.5 ppm (mg/kg diet) (aqueous tech.). ADI 10 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic in Ames and mouse lymphoma assays. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R38, R41| N; R50, R53
acifluorfen
EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R38, R41| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
acifluorfen-sodium
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 325 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 17, bluegill sunfish 62 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 77 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum >260, Anabaena flos-aquae >350 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for grass shrimps 189 mg/l. Bees Use not expected to result in honeybee exposure; tests not performed. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1800 mg/kg substrate. Other beneficial spp. Minimum inhibitory concentration for Azotobacter vinelandii >1000 ppm, for Bacillus subtilis 1000 ppm.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral application in rats, a fast and almost complete absorption and excretion occurs. Multiple application does not indicate a cumulative effect. The dermal resorption is low. Acifluorfen-sodium is judged not to present a substantial hazard to aquatic or terrestrial wildlife. Plants Not transported within the plant; degradation occurs at, or close to, the surface, DT50 c. 1 w. Metabolism is fast and extensive, through amination, hydroxylation and carboxylation. Soil/Environment The a.i. will be moderately quickly degraded, DT50 108 d (silt loam) - 200 d (clay loam), forming mainly bound residues and highly polar metabolites. Degradation occurs through microbial activity; there is also photolytic degradation on the soil surface. Accumulation in soil does not occur. Adsorption Koc 44-684, Kd 0.13-1.98; desorption Koc 131-1955, Kd 0.39-4.6. In water, acifluorfen is hydrolytically stable in the dark, but in light it is rapidly degraded, DT50 c. 2 h, forming mainly CO2.
|