|
abamectin
See also The BioPesticide Manual, 2nd Ed., entry 2:97
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 6; avermectin
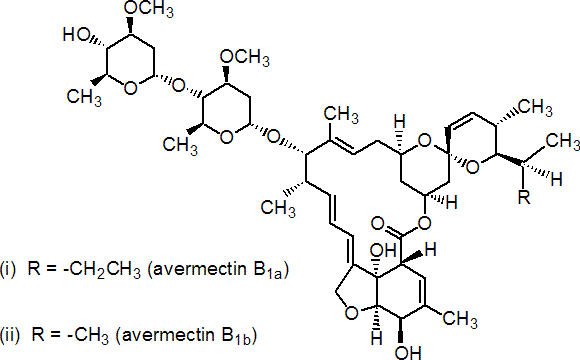
NOMENCLATURE
Common name: abamectin (BSI, draft E-ISO, ANSI); abamectine ((f) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name: (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S,13S,20R,21R,24S)-6'-[(S)-sec-butyl]-21,24-dihydroxy-5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-2-oxo-3,7,19-trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene-6-spiro-2'-(5',6'-dihydro-2'H-pyran)-12-yl 2,6-dideoxy-4-O-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-a-L-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-3-O-methyl-a-L-arabino-hexopyranoside (i) mixture with (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S,13S,20R,21R,24S)-21,24-dihydroxy-6'-isopropyl-5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-2-oxo-3,7,19-trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene-6-spiro-2'-(5',6'-dihydro-2'H-pyran)-12-yl 2,6-dideoxy-4-O-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-a-L-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-3-O-methyl-a-L-arabino-hexopyranoside (ii) (4:1)
Chemical Abstracts name: 5-O-demethylavermectin A1a (i) mixture with 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-25-(1-methylethyl)avermectin A1a (ii)
Other names: avermectin B1
CAS RN: [71751-41-2] (abamectin); [65195-55-3] (i); [65195-56-4] (ii)
EEC no.: 265-610-3 (avermectin B1a); 265-611-9 (avermectin B1b)
Development codes: MK-0936 (Merck & Co.); C-076 (Ciba); L-676,863
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition: A mixture containing ³80% avermectin B1a (i) and £20% avermectin B1b (ii).
Mol. wt.: 873.1 (avermectin B1a); 859.1 (avermectin B1b)
M.f.: C48H72O14 (avermectin B1a); C47H70O14 (avermectin B1b)
Form: Colourless to pale yellow crystals.
M.p.: 161.8-169.4 °C (decomp.)
V.p.: <3.7 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C)
KOW: logP = 4.4?.3 (pH 7.2, room temperature)
Henry: 2.7 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C)
S.g./density: 1.18 (22 °C)
Solubility: In water 7-10 mg/l (20 ºC). In toluene 350, acetone 100, isopropanol 70, chloroform 25, ethanol 20, methanol 19.5, n-butanol 10, cyclohexane 6 (all in g/l, 21 ºC).
Stability: Stable to hydrolysis in aqueous solutions at pH 5, 7, and 9 (25 ºC). Sensitive to stronger acid and base. U.V. irradiation causes conversion first to the 8,9-Z- isomer, then to unidentified decomposition products.
Specific rotation: [a]D22 +55.7?(c=0.87, CHCl3)
COMMERCIALISATION
Production: Isolated from fermentation of Streptomyces avermitilis, a naturally occuring soil Actinomycete.
History: Anthelmintic and acaricidal activity of a group of chemically related compounds, the avermectins, reported by I. Putter et al. (Experientia, 1981, 37, 963). A mixture of two of these, avermectin B1a (i) and avermectin B1b (ii) introduced in 1985 as an acaricide and insecticide by Merck Sharp & Dohme Agvet (now Syngenta AG).
Manufacturers: Jingma; Sharda; Sinon; Syngenta; Tide
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry: Acts by stimulating the release of g-aminobutyric acid, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, thus causing paralysis. See M. J. Turner & J. M. Schaeffer in Ivermectin and Abamectin, W. C. Cambell ed., Springer-Verlag, New York (1989) p. 73.
Mode of action: Insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Has limited plant systemic activity, but exhibits translaminar movement.
Uses Control of motile stages of mites, leaf miners, suckers, Colorado beetles, etc. on ornamentals, cotton, citrus fruit, pome fruit, nut crops, vegetables, potatoes, and other crops. Application rates are 5.6 to 28 g/ha for mite control, 11 to 22 g/ha for control of leaf miners. Also used for control of fire ants.
Phytotoxicity: May be phytotoxic to pome fruit when mixed with captan.
Formulation types: EC.
Compatibility: Not compatible with captan.
Selected products: 'Agrimec' (Syngenta); 'Dynamec' (Syngenta); 'Vertimec' (Syngenta); 'Abacide' (Mauget); 'Abamex' (Vapco); 'Biok' (Cequisa); 'Gilmectin' (Gilmore); 'Romectin' (Rotam); 'Satin' (Sanonda); 'Timectin' (Tide); 'Vibamec' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Affirm' (fire ant control) (Syngenta); 'Agri-Mek' (citrus) (Syngenta); 'Avid' (ornamentals) (Syngenta); 'Clinch' (Syngenta); 'Zephyr' (cotton) (Syngenta); 'Agromec' (Chemvet); 'Apache' (AFRASA); 'Belpromec' (Probelte); 'Crater' (AFRASA); 'Vamectin 1.8 EC' (IQV); 'Vapcomic' (Vapco); 'Vivid' (Florida Silvics)
Discontinued products: 'Agrimectin' * (Agro Chemicals)
ANALYSIS
Product: analysis by hplc with u.v. detection.
Residues: by conversion to a fluorescent product followed by hplc with fluorescence detection. See T. Wehner et al. in Comp. Anal. Profiles, Chapt. 4.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews: FAO/WHO 74, 80, 82 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). G. Lankas & L. R. Gordon in Toxicology in Ivermectin and Abamectin, W. C. Campbell ed., Springer-Verlag (1989) pp. 89-112.
Oral: Acute oral LD50 (in sesame oil) for rats 10, mice 13.6 mg/kg; (in water) for rats 221 mg/kg.
Skin and eye: Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits).
ADI: (JMPR) 0.002 mg/kg b.w. [1997] (for sum of abamectin and 8,9-Z- isomer); 0.001 mg/kg b.w. [1995] (for residues not containing D-8,9-isomer).
Other: Non-mutagenic in the Ames test.
Toxicity class: EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds: Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 84.6, bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg.
Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.2, bluegill sunfish 9.6 mg/l.
Daphnia: EC50 (48 h) 0.34 ppb.
Algae: (72 h) for Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata >100 mg/l.
Other aquatic spp.: LC50 (96 h) for pink shrimp (Panaeus duorarum) 1.6, blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) 153 ppb.
Bees: Toxic to bees.
Worms: LC50 (28 d) for earthworms 28 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: Rapidly eliminated (80-100% in 96 h), mainly via faeces; urinary excretion was 0.5-1.4%.
Plants: Degradation/metabolism in each of three different plants is similar and occurs predominantly by photolysis on the plant surfaces. The definition of the residues is thus expressed as the combined residues of avermectin B1 and its 8,9-Z-avermectin B1 photoisomer.
Soil/Environment: Binds tightly to soil, with rapid degradation by soil micro-organisms. No bioaccumulation.
|