|
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
Herbicide
HRAC O WSSA 4; phenoxycarboxylic acid
NOMENCLATURE
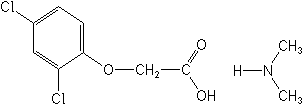
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
IUPAC name dimethylammonium (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetate
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
Mol. wt. 266.1 M.f. C10H13Cl2NO3 M.p. decomp. c. 120 °C Solubility In water 3 kg/l (20 ºC). Soluble in alcohols and acetone. Insoluble in kerosene and diesel oil.
COMMERCIALISATION
History The potent effects of its salts on plant growth were first described by P. W. Zimmerman & A. E. Hitchcock (Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst., 1942, 12, 321), and its early history is covered in The Hormone Weedkillers, C. Kirby (1980). Manufacturers Agrochem; Ancom; Atanor; Atul; CAC; Crompton; Crystal; Dow AgroSciences; Krishi Rasayan; Marks; Nitrokémia; Nufarm GmbH; Nufarm Ltd; Nufarm UK; Proficol; Sannong; Sharda; Sundat; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide. Salts are readily absorbed by the roots, whilst esters are readily absorbed by the foliage. Translocation occurs, with accumulation principally at the meristematic regions of shoots and roots. Acts as a growth inhibitor. Uses Post-emergence control of annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds in cereals, maize, sorghum, grassland, established turf, grass seed crops, orchards (pome fruit and stone fruit), cranberries, asparagus, sugar cane, rice, forestry, and on non-crop land (including areas adjacent to water), at 0.28-2.3 kg/ha. Control of broad-leaved aquatic weeds. The isopropyl ester can also be used as a plant growth regulator to prevent premature fruit fall in citrus fruit. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to most broad-leaved crops, especially cotton, vines, tomatoes, ornamentals, fruit trees, oilseed rape and beet. Formulation types EC; GR; SP; SL.
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
Selected products: 'Baton' (Nufarm Ltd); 'Ded-Weed' (Crompton); 'Dioweed' (United Phosphorus Ltd); 'DMA 6' (Dow AgroSciences); 'DMA-4' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Haybob II' (Barclay); 'Sanaphen D' (SL) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Spritz-Hormin' (Nufarm GmbH); 'Staff' (Headland); mixtures: 'Erbitox Combi' (+ MCPA-dimethylammonium) (Siapa); 'Lancet' (+ fluroxypyr-2-butoxy-1-methylethyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'U 46 Combi Fluid' (+ MCPA-dimethylammonium) (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
'Agro D-Amin' (AgroSan); 'Depitox' (Nufarm UK); 'Desormone' (Bayer CropScience); 'Dicopur' (Nufarm GmbH); 'Dri-Clean' (Riverdale); 'Fito amina' (Agricultura Nacional); 'Formula 40' (mixture with triisopropanolammonium) (Dow AgroSciences, Bayer CropScience); 'Herboxone' (Marks, Headland); 'HY-D' (Agrichem Int.); 'Saber' (Platte); 'Savage' (Platte); 'Weed Rhap A-4D' (Helena); 'Weedar 64' (Nufarm Ltd); 'Weedar IVM 44' (Nufarm Ltd) mixtures: 'Dicopur Combi' (+ MCPA-dimethylammonium) (Nufarm GmbH); 'DPD-Amine' (+ dichlorprop-dimethylammonium) (Nufarm Ltd); 'Range' (+ dicamba-dimethylammonium) (Albaugh); 'Weedmaster' (+ dicamba-dimethylammonium) (BASF, Syngenta) Discontinued products mixtures: '2 Plus 2' * (+ mecoprop) (
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of 2,4-D, salts, esters and mixed combination products by acid-base titration, by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2060, 2257; 1994, F, 292-319; Herbicides 1977, pp. 6-21), by rplc (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 971.07, 976.03, 978.05, 984.07; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2060; 1988, D, 51), by hplc (ibid., 1983, 1757), or by i.r. spectrometry (ibid., 1998, H, 131). Free phenol impurity determined by glc (CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 197), hplc (ibid., 1994, F, 362) or electrochemically (ibid., 1994, F, 368). Residues determined by glc of derivatives (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, I, 201-D; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 630) or by hplc (M. Meier et al.,Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem.,1989, 334, 235). In drinking water, by conversion to methyl ester with diazomethane, then glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.32).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77, 79, 80, 82, 92 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Toxicity and hazards to man, domestic animals and wildlife have been reviewed (J. M. Way, Residue Rev., 1969, 26, 37). IARC ref. 15, 41; Suppl. 7 class chlorophenoxy herbicides classified as 2B, based on epidemiology of production. More recent evidence (M. Kogevinas et al., Am. J. Epidemiol., 145(12), 1061 (1997)) relates this to dioxin contamination of early production. Not relevant to current processes.
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
Oral Acute oral LD 50 for rats 949 mg/kg. Skin and eye LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg; not a skin irritant (rabbits); severe irritant to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.5 mg/l air.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
2,4-D-dimethylammonium
Birds Acute oral LD 50 for bobwhite quail 500 mg/kg. Oral LC50 for bobwhite quail >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 100 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum 51.2 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 µg/bee; (oral) c. 94 µg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
2,4-D
EHC 29 (WHO, 1984), 84 (WHO, 1989). EHC 84 concludes that, when used as recommended, 2,4-D does not appear to produce direct toxic effects on any animal species. Animals In rats, following oral administration, elimination is rapid, and mainly as the unchanged substance. Following single doses of up to 10 mg/kg, excretion is almost complete after 24 hours, although, with higher doses, complete elimination takes longer. The maximum concentration in organs is reached after c. 12 hours. Plants In plants, metabolism involves hydroxylation, decarboxylation, cleavage of the acid side-chain, and ring opening. Soil/Environment In soil, microbial degradation involves hydroxylation, decarboxylation, cleavage of the acid side-chain, and ring opening. Half-life in soil <7 d. Koc c. 60. For a review of environmental aspects of 2,4-D, see Environmental Health Criteria 84 (WHO, 1989). Rapid degradation in the soil prevents significant downward movement under normal conditions.
|